FCC Mandate: Internet Providers’ “Nutrition Facts” Labels
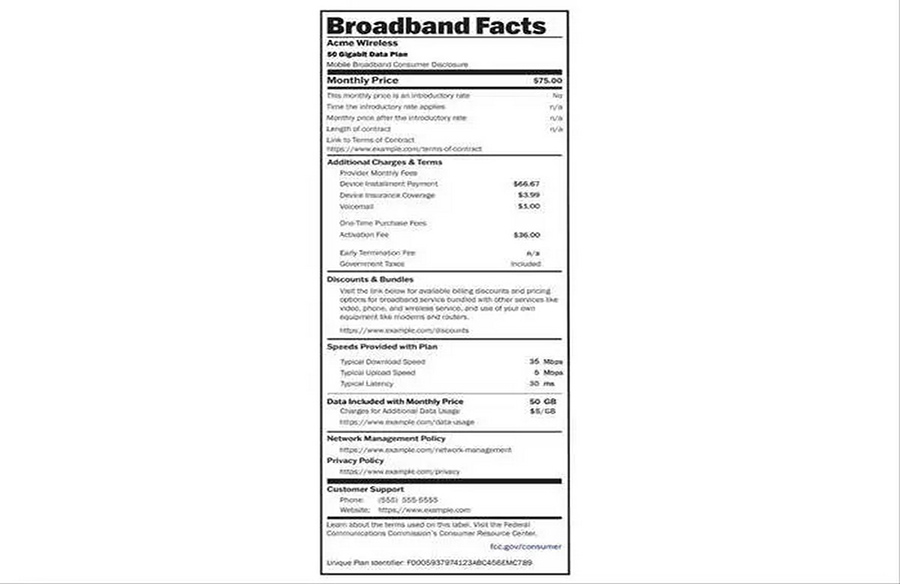
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has introduced a new requirement for internet providers to offer customers detailed breakdowns of fees and speeds akin to a “nutrition facts” label, aiding consumers in understanding their internet plans better.
Overview of the FCC Mandate
Internet providers with over 100,000 customers are mandated to present consumers with a simplified breakdown of costs, fees, and speeds associated with their plans. This format, resembling nutrition labels found on consumer products, aims to enhance transparency and enable informed decision-making.
Implementation and Timeline
Commencing Wednesday, larger internet companies must display these labels prominently at all points of sale, whether online or in physical stores. Smaller providers, with fewer than 100,000 customers, have until October to comply with the mandate.
Accessibility and Customer Reach
Importantly, the labels are not limited to new customers but must also be accessible to existing customers through online account portals. Additionally, providers are obligated to furnish the label upon customer request.
Detailed Information on Labels
The mandated labels must contain comprehensive information, including introductory rates, data allowances, contract duration, early termination fees, and other pertinent details. Moreover, they must include links to further resources regarding network management practices and privacy policies.
Purpose and Benefits
According to the FCC, these “Broadband Labels” are designed to offer clear, user-friendly, and accurate insights into the cost and performance of high-speed internet services. Modeled after FDA nutrition labels, they facilitate consumer comparison shopping, aiding individuals in selecting internet plans that align with their needs and budget.
Evolution of the Labeling Requirement
The concept of broadband labels resembling nutrition facts was first proposed as a voluntary option in 2016. However, it became a mandatory directive in 2022 following congressional action under the 2021 infrastructure law. This move underscores a broader effort to enhance consumer protections and promote transparency in the telecommunications sector.
Industry Response and Compliance
Several internet service providers (ISPs) have proactively implemented the labels ahead of the FCC’s deadline. Notable examples include Google Fiber, which introduced the labels in October, and Verizon, which followed suit in the preceding month. Such initiatives reflect a growing industry commitment to transparency and consumer empowerment in the digital age.





















